IRB Knowledge Center
IRB Basic Information
What is the IRB?
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) is responsible for the review and monitoring of all research involving human subjects taking place at Georgetown University. As part of this review process, the IRB balances both ethical considerations and scientific validity to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects. IRB is an acronym for Institutional Review Board. The IRB is responsible for the review and approval of all research involving human subjects, as well as scientific validity and ethical review.
When do I have to submit to the IRB?
If you plan to conduct human subjects research, you must submit to the IRB and receive approval prior to beginning any research.
Human subject is defined by the Common Rule as meaning “a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research:
- Obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the information or biospecimens; or
- Obtains, uses studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable bio specimens. (45 CFR 102(e)(1))
Research is defined as “means a systematic investigation, including research development, testing, and evaluation, designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.” (45 CFR 46.192(l))
How do I submit a study to the IRB?
All projects requiring or requesting a formal determination must be submitted through the electronic IRB system.
For information on how to access the IRB system, as well as additional information, reference guides, FAQs, log-in guidance, and more see the Georgetown-MedStar IRB System page.
How is my submission reviewed?
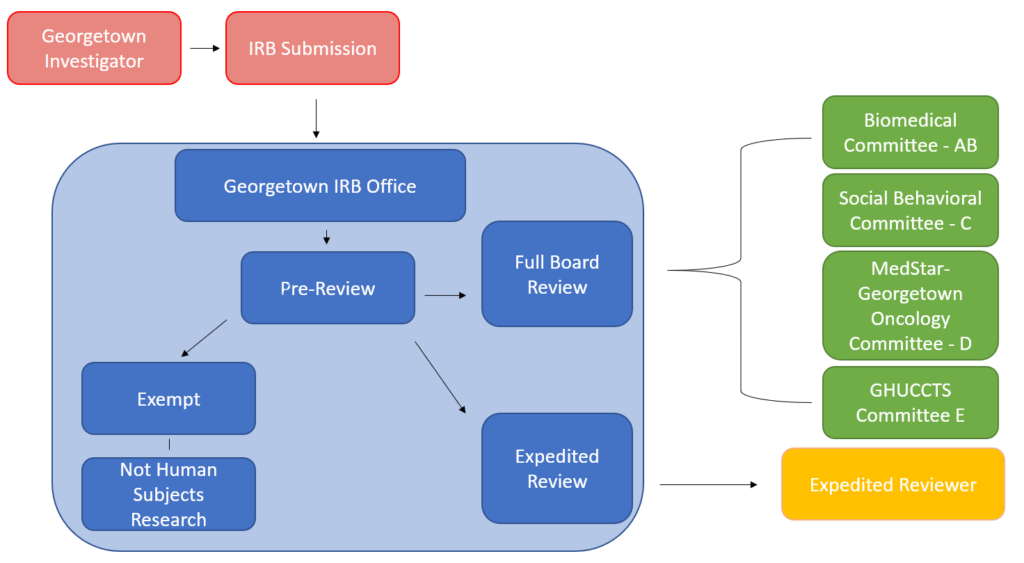
Upon your formal submission, the GU IRB office will conduct a pre-review of your submission. During the pre-review process, the GU IRB office will confirm the following:
- Inclusion of Georgetown protocol and sufficient information provided
- Inclusion of subject facing documents
- Determine the appropriate level of IRB oversight
- Confirm completion of Human Subjects Research training and necessary Ancillary Reviews
After pre-review is completed, your submission will undergo the appropriate level of IRB review.
Is any training required to conduct human subject research?
For detailed information and instructions, please see our Training and Education page.
What is not human subjects research?
IRB oversight is limited to human subjects research as indicated in the “When do I have to submit to the IRB?” section. Therefore, research that is not human subjects research is not within the scope of IRB review.
If you are not certain whether your research project is human subject research or you would like for the IRB Office to make a formal determination, please complete and submit a IRB submission with the protocol attached in the Georgetown-MedStar IRB system.
Formal IRB determinations and Not Human Subjects Research letters will only be provided through the review process in the Georgetown-MedStar IRB system. Formal determinations will not be provided through email or Virtual Office Hours. Upon submission, if the IRB does not agree with you that your research project is not human subject research, you will be asked to submit a full IRB application in the Georgetown-MedStar IRB system. Do not assume that your research project is not human subjects research.
What are quality improvement projects?
(QI) projects can be similar to the type of human subjects research that the IRB needs to review. While QI projects often include activities such as conducting surveys, reviewing identifiable data, drawing conclusions about problems, and suggesting methods for improvement, QI projects may not require IRB oversight. However, depending on the implementations and goals of the project, there may be a human subjects research element and the QI project may require IRB review.
Therefore, it is highly recommended to submit all QI projects to the IRB for a formal determination. If you are not certain whether your quality improvement project includes human subject research, please complete and submit the IRB application with the protocol attached in the Georgetown-MedStar IRB system. Do not assume that your quality improvement project is not human subjects research.
What is exempt research?
The Common Rule allows for a certain subset of human subjects research to be exempt from IRB oversight. There is not a separate application for this type of research and the IRB office will request the appropriate necessary information during the pre-review process. This research must be submitted to the IRB for a formal letter of exemption prior to the beginning of any research. Please note that exempt research still requires adherence to GU institutional policy surrounding research. Per GU policy, the IRB is the only entity who can make a determination of exemption.
For more details regarding what research may qualify for an exempt determination.
What is expedited review?
Human subjects research can fall under what the Common Rule refers to as expedited review. Expedited review requires review by a single expedited reviewer rather than review by the entire IRB committee. Research that is determined to qualify for expedited review during the pre-review process will be forwarded to an appropriate IRB reviewer.
For details regarding what research may qualify for expedited review.
What is full board review?
Human subjects research that does not fall under any other category will go to full board review. Upon submission to the IRB, the IRB Office will determine the appropriate committee that will review the submission.
For details regarding each IRB committee.
Where can I find information related to a specific committee?
Georgetown IRB has four IRB committees, three biomedical and one social/behavioral. Each committee is composed of members from both scientific and non-scientific backgrounds. For information regarding each committee see the IRB Committees page.
Where can I find information about IRB Policies, Procedures, and Guidance?
For information regarding the IRB’s policies and procedures, manuals, regulations, and guidance see the Policies, Procedures, and Guidance page.
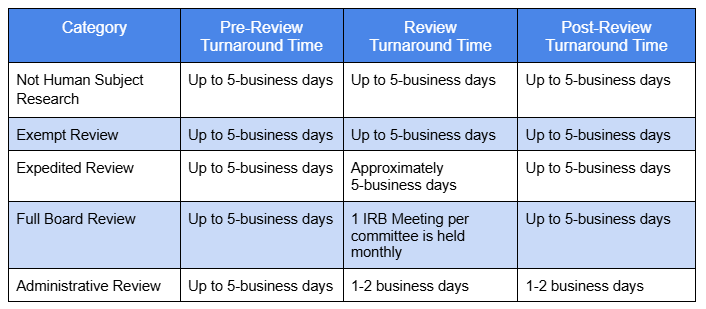
What are the timelines for review?
The IRB approval timeline can vary heavily depending on the number of submissions currently being processed by the IRB. The IRB recommends submitting well in advance of any deadlines or requirements. While the IRB strives to process submissions as quickly as possible, the time until completion may vary greatly based on the complexity of the study, responsiveness of the study team, and general workload of the IRB.
New IRB submissions enter the queue of the IRB where they undergo pre-review on a roughly first come first serve basis. The IRB aims to provide a first round of clarifications requested within approximately 5 business days. Once the study team provides the requested clarifications, the submission will re-enter the queue. It is important to note that all clarifications requested should be addressed prior to resubmitting to the IRB. Unaddressed clarifications will result in the submission being returned to the study team. This process will continue until pre-review is completed.
Please note that incomplete IRB submissions, CITI training requirements, COI disclosures, and ancillary review requirements will hold up an IRB submission from proceeding and result in the submission being returned to the study team.
Once pre-review is completed, the IRB submission will be processed under the appropriate level of IRB oversight.
For submission requiring full board review, pre-review should be completed prior to the committee meeting deadline to guarantee timely full board review. See: IRB Committees
After the submission is reviewed, please expect to receive a determination letter within 5 business days.
Note: If you are doing research outside of the United States, please see the International Research page for additional timeline considerations.